Zhang B, Yuan Q, Sun R, et al. Insights into the effects of Zn exposure on the fate of tylosin resistance genes and dynamics of microbial community during co-composting with tylosin fermentation dregs and swine manure[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(12): 14423-14433.
Insights into the effects of Zn exposure on the fate of tylosin resistance genes and dynamics of microbial community during co-composting with tylosin fermentation dregs and swine manure
Bo Zhang , Qingbin Yuan , Meng Meng Wang, Ruonan Sun, Huiling Liu , Peng Wang
期刊:Environ Sci Pollut Res IF:4.223
作者单位:哈尔滨工业大学 城市水资源与环境国家重点实验室
关键词:
抗生素抗性基因;协同;毒物兴奋效应;泰乐菌素发酵渣;锌。
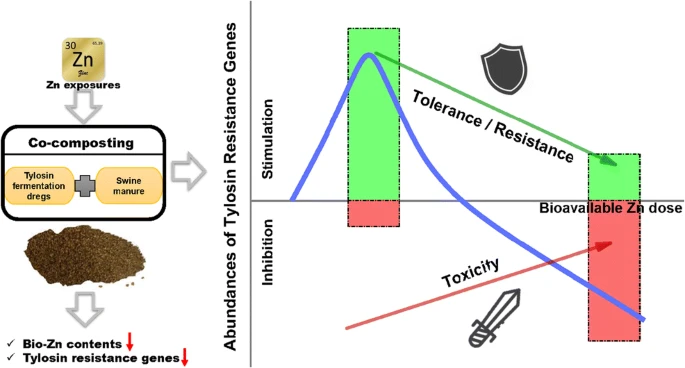
文章摘要
虽然重金属被广泛报道会导致抗生素耐药性的传播,但抗生素耐药性如何随重金属丰度的变化仍不清楚。在这项研究中,泰乐菌素发酵渣(TFDs)和猪粪混合堆肥工艺采用了两种重金属锌暴露水平。结果表明,共堆肥完成后,生物有效锌含量平均降低2.6倍,总泰乐菌素抗性基因的去除率约为23.5%。此外,泰乐菌素抗性基因和一些普通细菌可能表现出类似于激素的剂量反应,在共堆肥过程中,生物有效锌含量诱导了高剂量抑制和低剂量刺激,这代表了对有害环境刺激的适应性反应的有利方面。这项研究为锌污染固体废物处置提供了全面的理解和预测风险评估,并建议低水平的锌或其他重金属应受到更多关注,因为它们可能诱导耐药细菌和传播抗生素耐药基因。
启因生物-应用qPCR探索微生物世界